Open Circuit vs Closed Circuit: What's The Difference
An electrical circuit effectively has just two states; open and closed.
Table of Contents
An open circuit will not allow electrical current to flow, no lights will turn on, no socket outlets will work, no equipment will function. A closed circuit will enable electrical current to flow around the circuit meaning that equipment, lamps, appliances and other electrical equipment will work.
Back to top1) What is a Closed Circuit?
A closed circuit provides a complete circuit with a continuous path for electrical current to flow from the power source back to itself. In this normal condition, electrons can move freely through conductors, creating a continuous current flow that powers electrical devices.
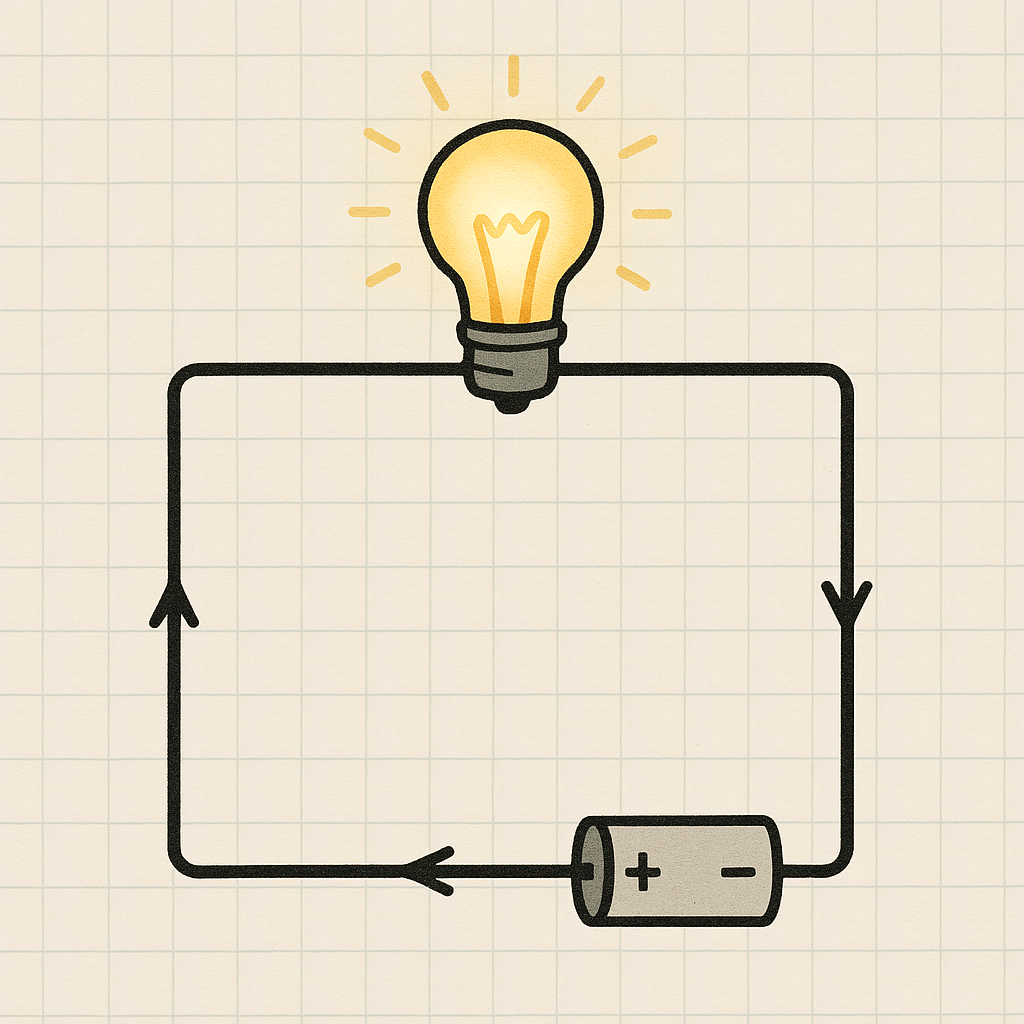
Think of a closed circuit like a closed pipe system where water flows continuously in a loop. The power supply acts as a pump, pushing electrons through the current path just as hydraulic pumps move water through pipes in a hydraulic system. This closed position of the circuit allows flow of electric current to reach all connected components.
In a properly functioning closed circuit, the total circuit current flows according to Ohm's Law, which states that current equals voltage divided by resistance. The energy source maintains a voltage difference across the circuit, driving the flow of electrons through metal atoms in conductors.
Back to top2) What is an Open Circuit?
An open circuit occurs when there's a break in the continuous path, preventing the flow of electricity. In this open circuit condition, the circuit has almost infinite resistance at the break point, causing current to stop flowing entirely. The open circuit resistance becomes so high that zero current can pass through.
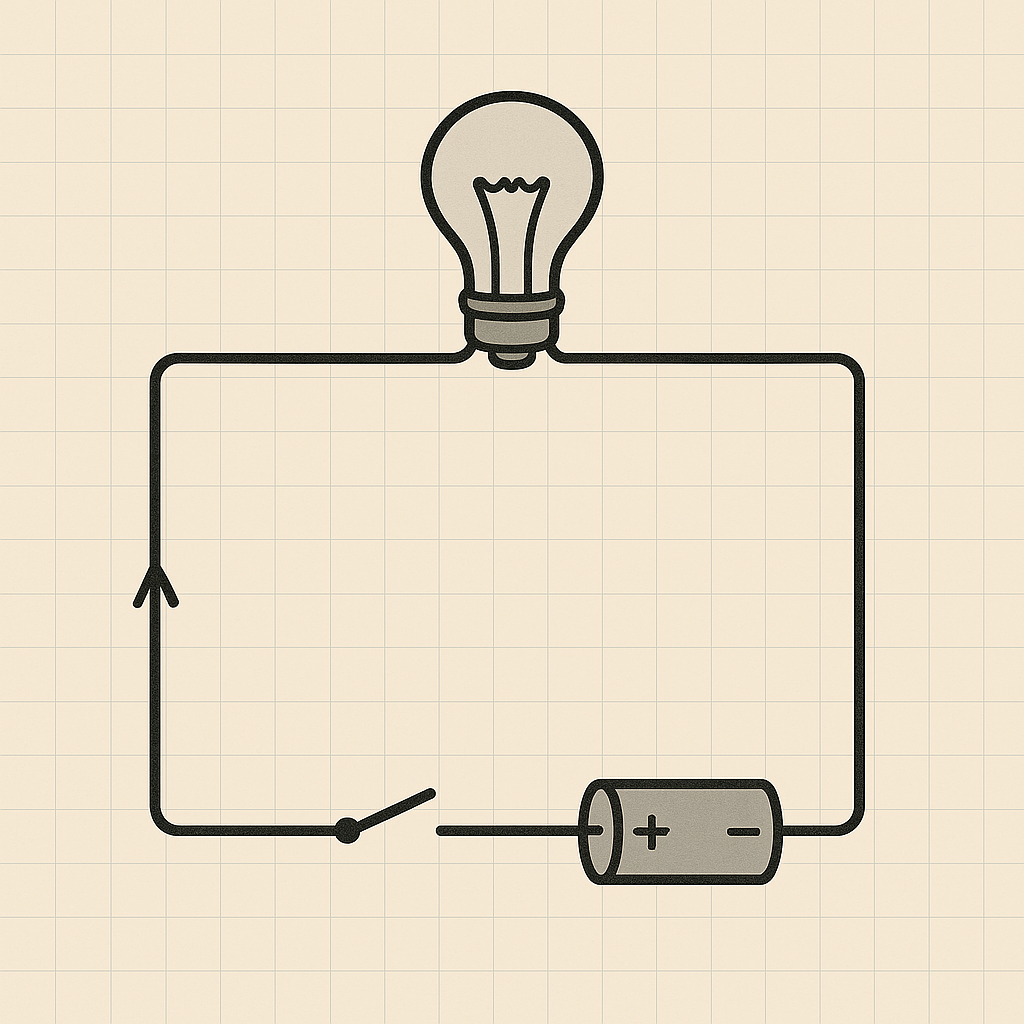
Using our water analogy, an open circuit is like an open pipe with a break - water cannot complete its journey and flow stops. Similarly, when electrical current encounters an open circuit, the flow of current ceases because there's no complete circuit for electrons to travel through.
Back to top3) Key Differences Between Open and Closed Circuits
The major difference between these states of an electric circuit lies in their ability to conduct electricity:
Closed Circuit Characteristics:
- Provides a closed path for current flow
- Maintains continuous current flow
- Powers electrical devices effectively
- Has finite resistance values
- Allows high current flows when needed
Open Circuit Characteristics:
- Breaks the current path
- Results in zero current flow
- Prevents electrical devices from operating
- Creates infinite resistance at the break
- Stops all electrical activity
4) Common Causes of Open Circuits
The occurrence of open circuits can result from various factors or electrical problems that interrupt the continuous path:
Physical Damage
A broken wire is one of the most common causes of accidental open circuits. When a conductor breaks, it creates a gap that prevents the flow of electrons. This component failure immediately converts a functioning closed circuit into an open circuit state.
Loose Connections
Loose connection points can create intermittent faults such as open circuits. Poor connections at terminals, especially at the negative terminals of a battery or power source, can cause the circuit to switch between open states and closed states unpredictably.
Component Failure
When a faulty component fails completely, it can create an open circuit within the device. This type of component failure requires replacement of the defective part to restore the complete circuit.
Intentional Disconnection
Safety devices like circuit breaker systems and emergency stop buttons are designed to create open circuits when necessary. These protective measures prevent dangerous high current flows that could damage equipment or pose safety risks.
Back to top5) Why Closed Circuits Are Essential
Closed loop systems are vital for electrical operation because they allow the power source to deliver energy to electrical devices. Without a complete circuit, the supply voltage cannot drive current through components, rendering them useless.
In electrical engineering, maintaining proper closed position connections ensures:
- Consistent voltage drop across components
- Proper operation of both series circuit and parallel circuit configurations
- Safe high voltages distribution in industrial applications
- Reliable performance of electronic appliance systems
6) Understanding Short Circuits
While open circuits prevent current flow, a short circuit creates the opposite problem by providing a path of least resistance that bypasses normal circuit components. This type of circuit fault occurs when current finds an unintended route with zero resistance, causing high current flows that can damage equipment.
Causes of Short Circuits
Short circuit conditions typically result from:
- Damaged insulation allowing conductors to touch
- Wrong hole connections on a solderless breadboard
- Pieces of metal creating unintended connections
- Moisture creating conductive paths between components
Short Circuit vs Open Circuit
Unlike an open circuit condition that stops current flow, short circuits allow excessive current to flow for a short time before protective devices like circuit breaker systems activate. This creates different impacts on electrical systems and requires different troubleshooting approaches.
Back to top7) Practical Applications and Examples
Understanding circuit diagram symbols and the behavior of electrical circuits helps in real-world applications:
Automotive Systems
A car battery provides the energy source for vehicle electrical systems. When connections become loose or wires break, open states prevent systems like lights or the radio transmitter from functioning.
Home Electronics
Electrical devices in homes rely on closed loop systems to function. A radio receiver, for instance, needs a complete circuit from the power supply to operate properly.
Industrial Equipment
Industrial applications often use complex electrical schematics showing series circuit and parallel circuit configurations. Quality components and proper maintenance prevent accidental open circuits that could shut down production.
Back to top8) Safety Considerations
The safety of electrical systems depends on understanding both open states and closed circuit conditions. Circuit breaker protection and proper component selection are essential for managing high voltages safely.
Emergency systems like emergency stop buttons create intentional open circuits to quickly shut down equipment when needed. This good idea prevents accidents and equipment damage in potentially dangerous situations.
Back to top9) Troubleshooting Circuit Problems
When electrical systems fail, checking for open circuit condition problems should be your first step. Use multi meters to measure current value and voltage sources to identify where the continuous path has been interrupted.
Look for:
- Broken wire connections
- Loose connection points
- Faulty component indicators
- Proper closed position of switches and breakers
10) To sum up…
Understanding the fundamental difference between open and closed circuits is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. Closed circuits provide the continuous current flow necessary for electrical devices to function, while open circuits prevent current flow entirely. Recognizing the distinct characteristics of each type of circuit helps in troubleshooting problems and maintaining safe, efficient electrical systems.
Whether dealing with simple low voltage circuits or complex high voltages industrial systems, the principles remain the same: electricity requires a complete circuit to flow, and any break in that path creates an open circuit condition that stops operation. By maintaining quality components and proper connections, you can ensure reliable continuous current flow in your electrical systems.
Back to top

